Open Data Portal
Custom Open Data Portal
As public administration institutions evolve, new areas emerge through which we perceive their transparency and the potential for residents to participate in the life of the authority. Making data available in an open format not only helps build trust in officials but also enables obtaining more specific answers on topics that require public consultations. Open data is also an excellent source for creating substantive materials that authorities can share through their social media accounts and wherever open communication forms the basis for social dialogue and collaboration with businesses.
Creating Open Data portals to disseminate access to public data is also in line with the guidelines of the European Commission (Directive 2013/37/EU) and the national development strategy in this area.
Functions that make the portal fully functional
There are various directions of data sharing – for residents, for businesses (G2B), and for other institutions (G2G). Each of them shares a common denominator grounded in both legal requirements and standards that we adhere to in the implementation of any other project. These common denominators are:
- Ease of access – primarily to the visual layer, also for individuals with disabilities, which we achieve through a simple, clear layout and the use of accessibility-enhancing elements such as high-contrast options, large fonts, or the capability for voice navigation within the site’s content.
- User-friendly interface – designed with the portal’s visitors in mind, both in the visual layer and in the API interface area.
- Understandable administrative panel structure – it enables easy and intuitive management of the portal and its content.
Visual data presentation backed by 20 years of business experience
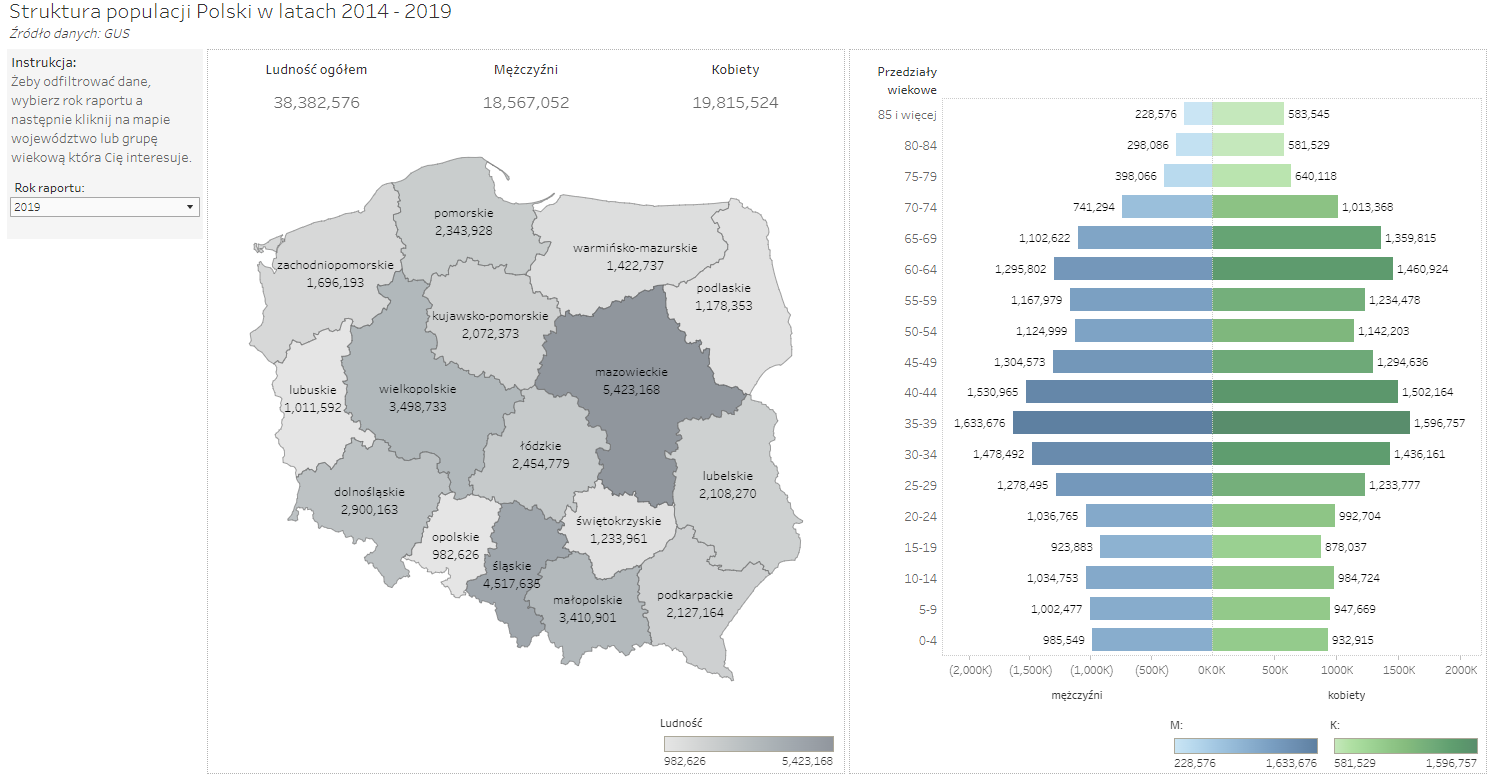
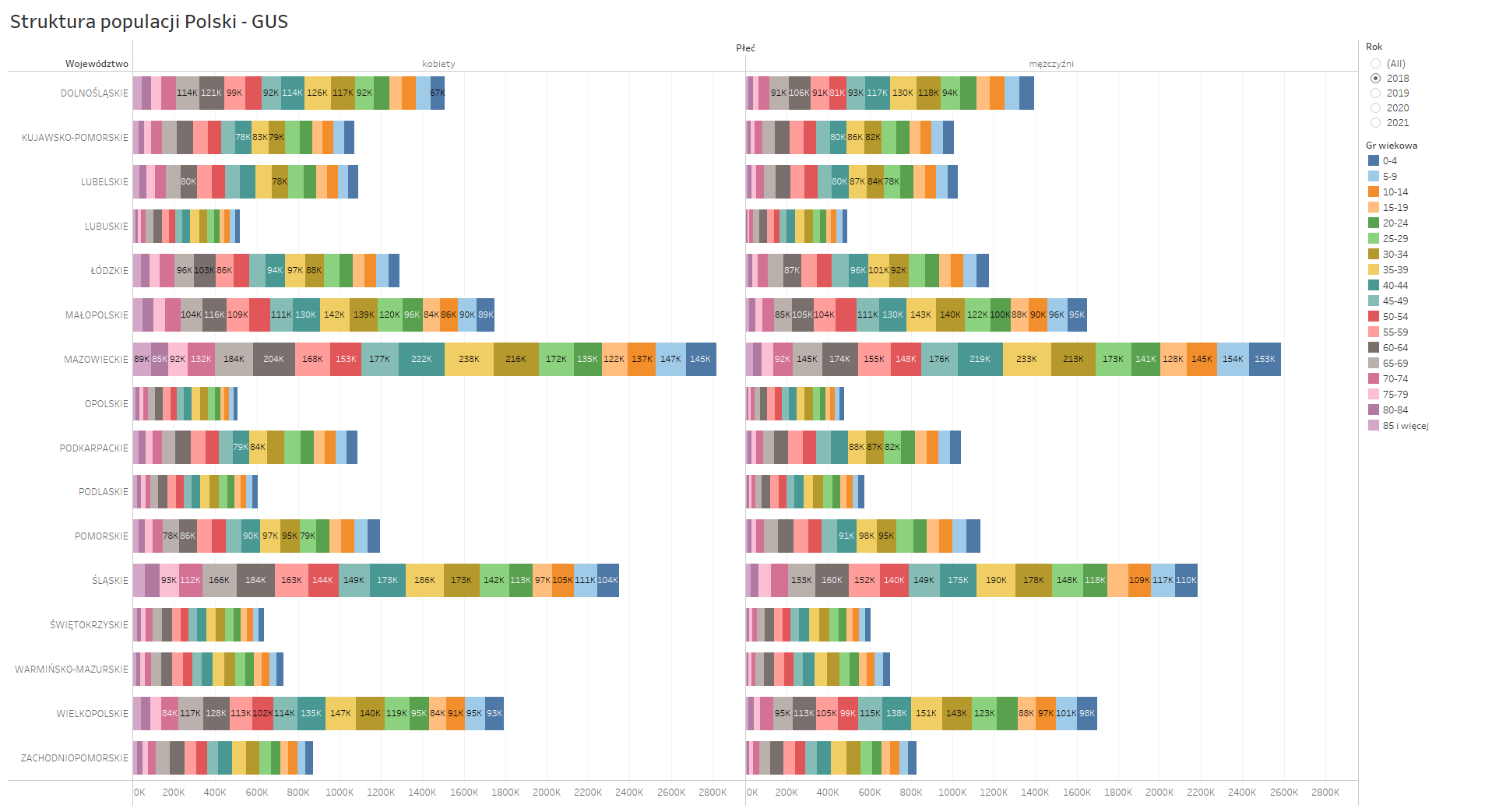
Almost any data can be presented in a way that is immediately understandable or in a manner that confounds any audience. As an example, consider the following visualizations presenting the same data.
The visualization, featuring a map, immediately informs us about the values of the key indicators upon the first interaction. Furthermore, it remains interactive, allowing users to click on a selected province and thereby filter the data on the adjacent chart. This chart also has the capability to filter data – by clicking on a specific age group, you can filter the values on the map to show where there are the most people in that age range.
The panel on the right side presents the same data as the aforementioned report. Although it does have interactive features for exploring and comparing the data, reading and analyzing such information in this format can be challenging.
At Astrafox, we have honed our skills in data analysis, visualization, and visual communication. How your portal appears from the user’s perspective and whether they feel comfortable trying to understand the materials intended for them directly impacts the image of your institution. An image, as we all know, can be easily tarnished but much more challenging to rebuild.
Other possibilities for an Open Data Portal
The open data sharing function often resides within an environment that serves an informational role around the stored resources. Therefore, additional components of the portal typically include:
- Structural data categorization, such as Demographics, Education, or Economy.
- Dataset descriptions.
- Information about data providers.
- The ability to browse datasets based on criteria like category, provider, format, resource type, etc.
- A news wall featuring updates and original articles related to the city or region.
- RSS feeds.
- Integration with Social Media.
- Alternative language versions.
- Other functions as per the requirements of the contracting party.